Description
3-MorpholinoPropanesulfonic Quick Details
Chemical Name: 3-MorpholinoPropanesulfonic
CAS No.: 1132-61-2
MolecularFormula: C7H15NO4S
Chemical Structure: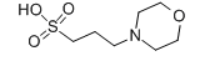
Molecular weight: 209.26
Assay: 99% min
3-MorpholinoPropanesulfonicTypical Properties
| Item | Specifications |
| Assay(CNO4S)(dried basis) | 99% min |
| pH of 1% solution at 25℃ | 2.5-4.5 |
| Heavy metals(as Pb) | 5ppm max |
| Fe content | 5ppm max |
| Loss on drying (105℃) | 0.5%max |
| pkaat 20℃ | 7.10-7.30 |
| Solution (10%)In water | Passes Test |
| Color of 1M·Solution(425nm,Hazen) | 50 max |
| UV Absorbance of a 0.1M Solution(1-cm path vs water)at 260 nm | 0.02 max |
Difference between MES and MOPS buffer
Introduction to Buffer Solutions in Biochemical Experiments
Buffer solutions play a crucial role in stabilizing the pH of systems during biochemical experiments. By maintaining a constant pH, buffers ensure the proper functioning of enzymes and other biochemical processes, making them indispensable in biological research.
MOPS vs. MES: A Comparison of Two Common Biological Buffers
MOPS (3-Morpholinopropanesulfonic acid) and MES (2-morpholineethanesulfonic acid) are both widely used buffers in biological experiments. Although they serve similar purposes, there are some key differences between them.
- MOPS has a buffer range of 6.5 to 7.9, making it suitable for use in experiments that require a neutral to slightly alkaline pH. It is often used in applications such as chloroplast thin-layer preparations for electron transfer and phosphorylation studies. Additionally, it is effective in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (IEF) and Northern Hybridization procedures, especially for RNA separation and membrane transfer.
- MES, on the other hand, is typically used in a slightly more acidic pH range and is often selected for experiments requiring stable pH under acidic conditions. Both buffers, however, are essential for a variety of biological applications, especially in maintaining the stability of pH-sensitive processes.
Applications of MOPS Buffer
- Biochemical Diagnostic Kits:
MOPS is commonly used as a biological buffer in biochemical diagnostic kits, including DNA/RNA extraction kits and PCR diagnostic kits, where pH stability is critical for accurate results. - Good’s Buffers for Biological Research:
MOPS is an essential ingredient in Good’s buffers, which are designed for biological research. These buffers help maintain the necessary pH environment for a range of biological reactions and experiments. - pH Stabilizing Agent:
In biological experiments, MOPS serves as an important pH stabilizing agent. It is often combined with a suitable weak acid and its conjugate base to create an effective buffer system. Most biological reactions require a neutral pH, typically between 6 and 8. Therefore, MOPS is particularly useful as it provides an effective buffer range within this range. - Non-Chelating Properties:
One of the key advantages of MOPS is that its acid-base form does not tend to chelate with certain metal ions, making it an ideal choice for experiments where metal ion interaction may interfere with results.
Packaging and Shipping
MOPS is typically packaged in 25 kg drums, which ensures safe handling and efficient storage.
Storage Instructions
To maintain its stability and effectiveness, MOPS should be stored in a ventilated, low-temperature drying environment. This helps preserve its quality and ensures that it remains effective for use in sensitive experiments







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.